San Joaquin Reaches a New Low
Courtesy of earthobservatory.nasa.gov
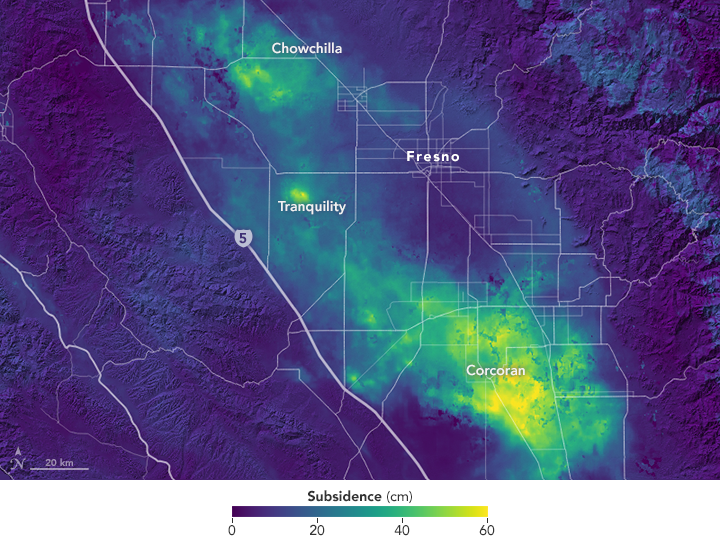
More yellow an area is on the image, the deeper the caving of the land is.
March 26, 2017
Everyone knows about the huge drought that has been affecting California for the past three years. Although California has been in a drought for hundreds of years, California’s dryness is at its highest since 1159. Not only is this damaging to California’s economy, but it has caused major problems that are beyond human control.
The drought has actually resulted in the sinking of the San Joaquin Valley due to the pumping of water from underground reservoirs called aquifers. Usually aquifers are filled with water which, in the San Joaquin Valley, comes from the Sierra Nevada. However, due to the drought, there is a shortage of water which causes the soil and rock to slowly sink down. The prediction is that the land will continue to sink at a rate of 2 inches/year, which is a lot more than it appears.The sinking causes the aquifers to become smaller, which lessens the amount of water they can hold. Due to this, even a flood would not be able to fully refill the aquifers or bring the land back up.
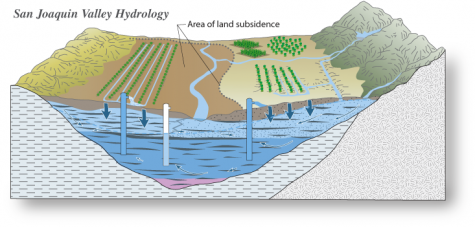
Aquifers are used to provide water for crops and provide fresh water.
According to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Corcoran and surrounding land are currently being affected by this. It has sunk about 22 inches in a little over a year, and the surrounding 60 miles are experiencing sinking as well. Another main spot is around El Nido where the land has sunk 16 inches. Each of these places had been known to be sinking before. However, new places have shown signs of subsidence including the area around Tranquility which has sunk 20 inches and other places scattered throughout the Sacramento Valley which are just starting to sink. Each of these subsidences (gradual caving of land) form a sort of bowl-shape.
So why is this such a big deal? The subsidences can lead to major damage on buildings, bridges, roads, canals, and other structures. It can also cause major damage to water transportation especially since the California Agency uses gravity to help move water from one location to the other. The sinking of the Valley is bound to affect the water flow. Additionally, the cost could be a huge problem. In fact, $100 million have been spent by the state and federal agencies on repairs beginning in the 1960s. One of the main ways to slow this would be to cut down on the amount of water that people use. Kennedy Maddock (10) was surprised when she learned what was happening and suggested, “To help save water.. we could have collecting containers to collect water from the rain and have it drain down to a water source.” Overall, the San Joaquin Valley and other places throughout California are suffering from the drought in more ways than just a shortage of water.
Sources: livescience.com, cnbc.com, and phys.org